Introduction
Do you ever experience jaw pain, clicking sounds when chewing, or frequent headaches around your temples? These could be signs of TMJ symptoms, a common condition affecting the temporomandibular joint — the hinge connecting your jaw to your skull.
TMJ disorders can disrupt daily life, making eating, speaking, or even yawning uncomfortable. In this article, we’ll explore the full spectrum of tmj symptoms, their causes, risk factors, and practical ways to manage the condition. With real-world examples and insights, you’ll understand how to recognize and address TMJ problems effectively.
What is TMJ and Why It Matters
Understanding the Temporomandibular Joint
-
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a hinge connecting the jawbone to the skull.
-
It allows you to move your jaw up, down, and side-to-side for talking, chewing, and yawning.
-
Any dysfunction or misalignment in this joint can lead to tmj symptoms, discomfort, or pain.
TMJ Disorders
-
TMJ disorders (TMD) encompass a range of conditions affecting jaw muscles, ligaments, or the joint itself.
-
Common causes include teeth grinding (bruxism), arthritis, stress, or jaw injury.
-
Statistics suggest that 10 million Americans experience TMJ disorders, with women being more prone than men.
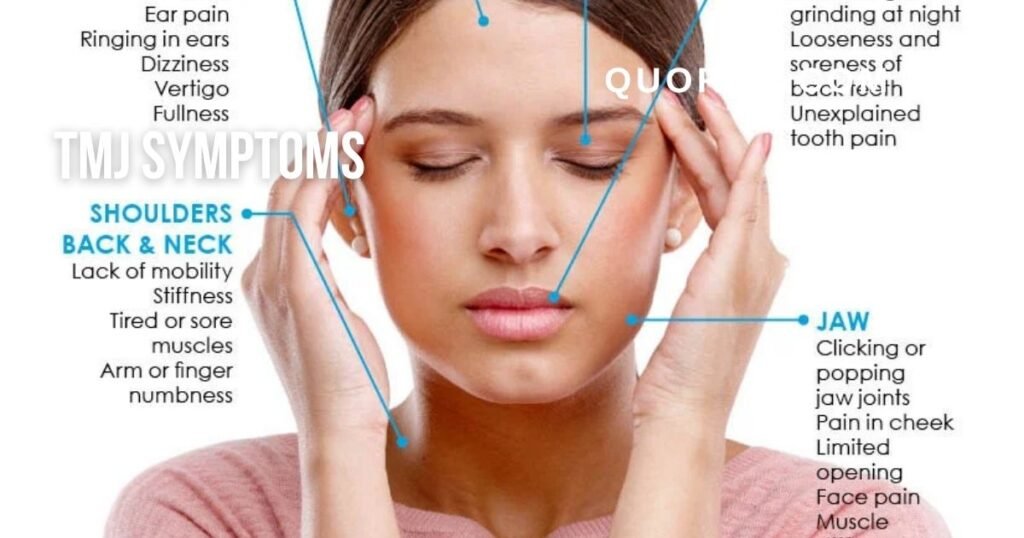
Common TMJ Symptoms
Jaw Pain and Tenderness
-
Pain or tenderness around the jaw joint is one of the earliest and most noticeable tmj symptoms.
-
Pain may worsen when chewing, talking, or opening your mouth wide.
Example: A patient reported soreness around the jaw after long workdays of stress, often feeling stiffness in the morning — a classic TMJ indicator.
Clicking, Popping, or Locking
-
Clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing your mouth are hallmark tmj symptoms.
-
Locking of the jaw, either open or closed, can make normal movements difficult.
Headaches and Facial Pain
-
TMJ disorders often cause tension headaches, earaches, or pain radiating to the temples and cheeks.
-
According to studies, up to 70% of TMJ patients report associated headaches.
Limited Jaw Movement
-
Difficulty opening the mouth fully or a feeling of your jaw “sticking” can indicate TMJ involvement.
-
This may affect daily activities like eating, speaking, and dental hygiene.
Ear-Related Symptoms
-
Ringing in the ears (tinnitus), pressure, or hearing sensitivity may accompany tmj symptoms.
-
These occur because the TMJ is close to the ear canal, and inflammation or dysfunction can radiate.
Other Related Symptoms
-
Neck or shoulder pain due to muscle tension.
-
Swelling on the side of the face.
-
Changes in bite or misalignment of teeth over time.
Causes and Risk Factors of TMJ Symptoms
Common Causes
-
Bruxism: Grinding or clenching teeth, especially during sleep.
-
Injury: Trauma to the jaw or head, including accidents or sports injuries.
-
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis affecting the TMJ.
-
Stress: High stress increases jaw muscle tension, aggravating TMJ problems.
Who Is at Risk?
-
Women aged 20–40 are most commonly affected.
-
People with chronic stress or anxiety.
-
Those with prior jaw injuries or misaligned teeth.
Diagnosis of TMJ Disorders
How Doctors Identify TMJ Problems
-
Physical examination of jaw movement and joint tenderness.
-
Listening for clicks or pops during movement.
-
Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs for joint evaluation.
Example: A patient experiencing jaw locking and headaches underwent an MRI that revealed displacement of the jaw disc, confirming TMJ disorder.
Treatment Options for TMJ Symptoms
Conservative Treatments
-
Resting the jaw: Avoid chewing gum or hard foods.
-
Heat or cold therapy: Relieves pain and inflammation.
-
Pain relief medications: Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen.
Dental and Physical Therapies
-
Mouthguards or splints: Prevent teeth grinding at night.
-
Physical therapy: Jaw exercises to improve mobility and reduce tension.
-
Dental corrections: Address bite misalignment if contributing to TMJ.
Advanced Interventions
-
In rare cases, injections (like corticosteroids) or surgical interventions may be necessary.
-
Surgery is usually a last resort when conservative treatments fail.
Lifestyle Tips to Manage TMJ Symptoms
-
Reduce stress through meditation, yoga, or relaxation techniques.
-
Avoid excessive chewing (gum, tough foods).
-
Maintain good posture to prevent neck and shoulder strain.
-
Apply gentle jaw exercises recommended by a physical therapist or dentist.
Conclusion
Understanding TMJ symptoms is essential for early detection and effective management. Jaw pain, clicking, headaches, and limited movement are all signals that should not be ignored. Most cases improve with conservative care, lifestyle adjustments, and dental support.
Also Read:
FAQs
Q1: Are TMJ symptoms permanent?
A: Most TMJ symptoms improve with conservative treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and stress management. Severe cases may require specialized care.
Q2: Can TMJ cause headaches?
A: Yes, tension headaches, migraines, and facial pain are commonly associated with TMJ disorders.
Q3: How is TMJ diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves physical examination, patient history, and sometimes imaging like X-rays or MRI.
Q4: Is TMJ more common in women?
A: Yes, research indicates that women between 20–40 are more likely to develop TMJ disorders.
Q5: Can lifestyle changes help TMJ?
A: Absolutely. Stress reduction, avoiding hard foods, and jaw exercises can significantly improve symptoms.